OVARIAN CYSTECTOMY (REMOVAL OF OVARIAN CYST)
When do I need removal of an ovarian cyst?
Large or persistent ovarian cysts, or cysts that are causing symptoms, usually need to be surgically removed. Surgery is also normally recommended if there are concerns that the cyst could be cancerous or could become cancerous. This procedure is called ovarian cystectomy.
How is ovarian cystectomy carried out?
An ovarian cystectomy is carried out by either a laparoscopy or a laparotomy (open procedure). These are usually carried out under general anaesthetic.
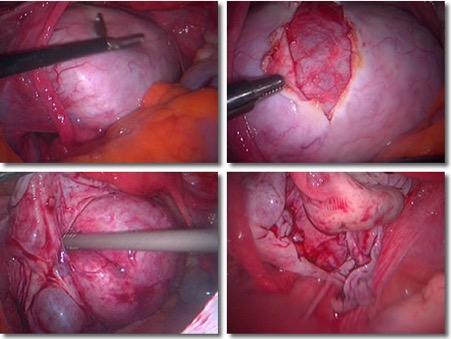
Laparoscopy
Most cysts can be removed using laparoscopy. This is a type of keyhole surgery where small cuts are made in your tummy and gas is blown into the pelvis to allow the surgeon to access your ovaries. A laparoscope (a small, tube-shaped microscope with a light on the end) is passed into your abdomen so the surgeon can see your internal organs. The surgeon then removes the cyst through the small cuts in your skin. Often the cyst may need to be drained (fluid from cyst taken out) in a closed bag, to make it smaller before removal through the cut in your skin. After the cyst has been removed, the cuts are closed using dissolvable stitches.
A laparoscopy is preferred because it causes less pain and has a quicker recovery time. Most women are able to go home on the same day or the following day.
Laparotomy
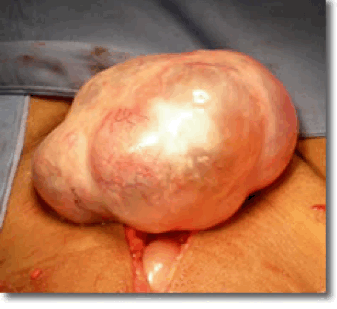
If your cyst is particularly large, or there’s a chance it could be cancerous, a laparotomy may be recommended. During a laparotomy, a single, larger cut is made in your tummy to give the surgeon better access to the cyst.
The whole cyst and ovary may be removed and sent to a laboratory to check whether it’s cancerous. Stitches or staples will be used to close the incision.
You may need to stay in hospital for a few days after the procedure.
What will happen after surgery?
After the ovarian cyst has been removed, you’ll feel pain in your tummy, although this should improve in a day or two. Following laparoscopic surgery, you’ll probably need to take things easy for two weeks. Recovery after a laparotomy usually takes longer, possibly around four to six weeks. If the cyst is sent off for testing, the results should come back in a few weeks and Mr Chattopadhyay will discuss with you whether you need any further treatment.
Contact Mr Chattopadhyay or your GP if you notice the following symptoms during your recovery: heavy bleeding, severe pain or swelling in your abdomen, a high temperature (fever), dark or smelly vaginal discharge. These symptoms may indicate an infection.


